AMD recently uncovered BIOS updates to enhance the performance of its Ryzen 9600X and 9700X processors. These updates tackle latency issues and come approximately a month after the initial Zen 5 desktop CPU reviews. Alongside these improvements, Windows 11 has been updated with optimized AMD-specific branch prediction for both Zen 4 and Zen 5 chips.
Addressing Latency Concerns
The new AGESA PI 1.2.0.2 firmware for AM5 motherboards targets “corner cases” where information sharing across different parts of a Ryzen 9 9000 processor required two transactions for reading and writing. AMD has successfully reduced this to a single transaction, effectively lowering core-to-core latency in multi-CCD models.
Performance Boost and New Power Option
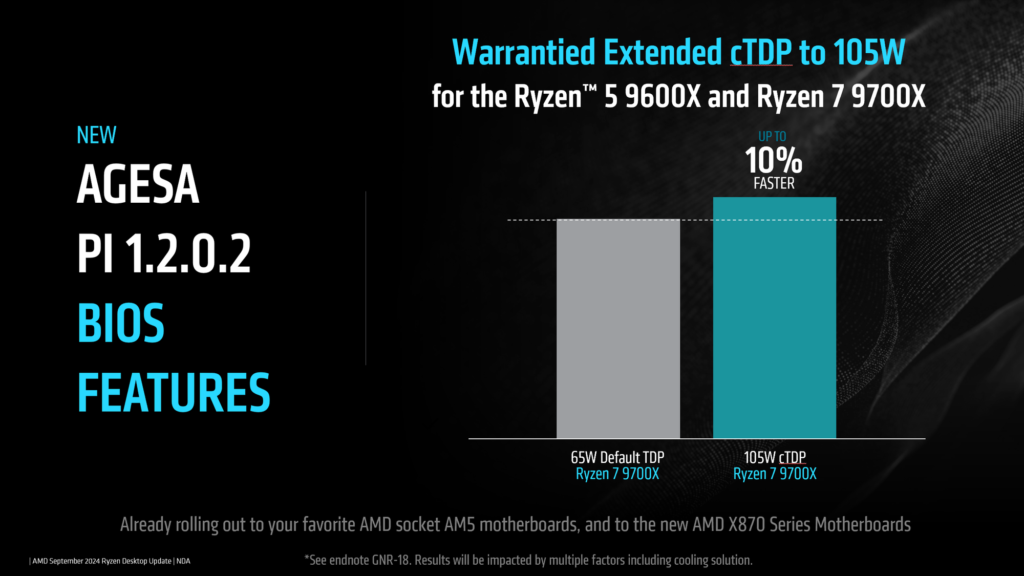
A notable addition is the 105-watt cTDP option for the Ryzen 9600X and 9700X. This increase in thermal design power has been validated since the processors’ release, ensuring it remains within design limits. Users can expect around 10 percent performance improvement, particularly in multithreaded workloads, without voiding their warranty. However, adequate cooling is essential when enabling this mode.
New Motherboards and Memory Support
This week also marks the launch of AMD’s X870 and X870E motherboards. While not mandatory for the latest Ryzen 9000-series CPUs, these boards offer standard USB 4.0 and simultaneous PCIe 5 Gen 5 support for graphics and NVMe. AMD hints at the importance of full PCIe Gen 5 support, possibly alluding to upcoming graphics card releases.
The new boards also support higher-clocked memory, with DDR5-8000 EXPO support now enabled. This upgrade provides 1 to 2ns latency improvements compared to DDR5-6000.





